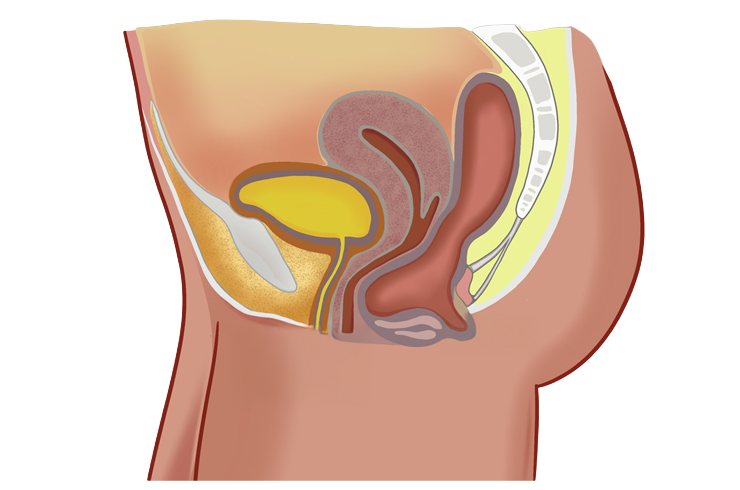
Rectocele: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
A rectocele is a condition where the rectal wall bulges into the vaginal canal due to weakening or damage of the supportive tissues between the rectum and vagina. This herniation typically occurs when the pelvic floor muscles and connective tissues become stretched or weakened, often as a result of childbirth, chronic constipation, heavy lifting, or aging. Rectocele is more common in women, particularly those who have had multiple vaginal deliveries or pelvic surgeries. The severity of a rectocele can vary, and while some women may remain asymptomatic, others may experience significant discomfort and functional issues.
Symptoms of rectocele include a sensation of vaginal bulging or fullness, difficulty with bowel movements, incomplete evacuation, and sometimes pain during intercourse. Women may notice the need to apply pressure to the vaginal wall to help pass stool. Diagnosis is usually made through physical examination and may be supported by imaging studies like defecography. Management depends on the severity of symptoms; mild cases are often treated with lifestyle modifications such as high-fiber diets, stool softeners, and pelvic floor exercises to strengthen supporting muscles. In more severe cases, surgical repair may be necessary to restore normal anatomy and relieve symptoms, improving quality of life.