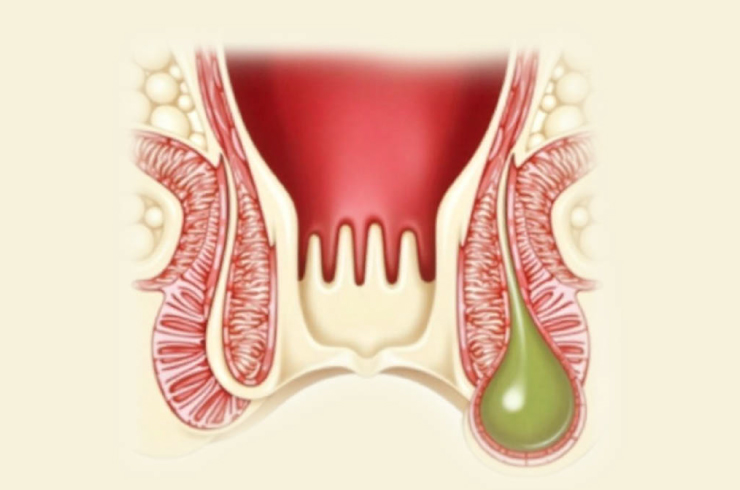
Perianal Abscess: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
A perianal abscess is a localized collection of pus that forms in the tissue around the anus and rectum due to infection of the anal glands. These glands can become blocked and infected by bacteria, leading to the rapid accumulation of pus. The condition can develop suddenly and is typically very painful, often presenting as a red, swollen, and tender lump near the anus. Additional symptoms may include fever, chills, fatigue, and difficulty sitting or walking. In some cases, the abscess may spontaneously drain, releasing foul-smelling pus, but often it continues to enlarge and worsen without proper medical intervention.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to avoid complications such as the development of a fistula-in-ano, where an abnormal tract forms between the anal canal and the skin. Treatment typically involves surgical drainage of the abscess under local or general anesthesia, which provides relief and prevents the spread of infection. Antibiotics may be prescribed if the patient has a weakened immune system or systemic infection, but drainage remains the mainstay of therapy. In recurrent or deep abscesses, further evaluation may be required to identify underlying fistulas. Good hygiene, a high-fiber diet, and regular follow-ups can help prevent recurrence and support healing.